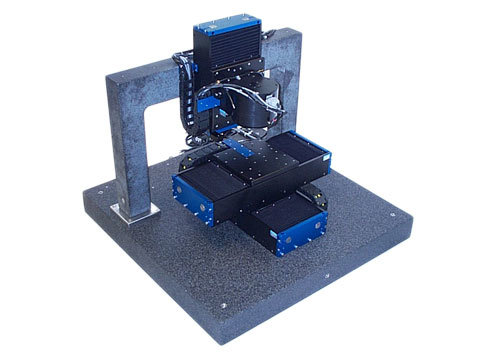
H2W Technologies has broad experience in designing and manufacturing Air Bearing actuators and positioning stages. Many of our standard products are also available in Air Bearing versions. In addition, H2W manufactures custom systems to meet the needs of specific and varied applications, including but not limited to semiconductor manufacturing, aerospace applications, and optics. These environments can vary in temperature from cryogenic temperatures to over 100 degrees Celsius, and H2W can design and supply actuators and positioning stages that can operate in these environments.
Considerations
- The air bearing stage is a precision device with sensitive components, it should not be mounted in an environment that is wet or excessively dirty. The air bearing stage should be in a clean environment at all times.
- The air bearing stage must not be operated in an environment with high ambient temperatures (>50??C).
- The system air supply must be free of oil and pressure fluctuations and should have a pre- filter and water removing trap upstream of the final filter/regulator unit for the stage. The final filter should be a 1-micron or better filter.
- The air bearing stage may be mounted in any orientation.
- The air bearing stage should be mounted to a flat and stiff surface. Some systems are assembled on a granite surface.
- When mounting the stage with the table moving vertically, it should be noted that the stage will be required to generate additional force due to gravity. If a vertical brake is not installed, the stage will slide down (drop) to the bottom hard stop when power fails.
- When the stage is not in use, it is recommended that airflow to the bearings be turned off in order to conserve air and avoid introducing contamination to the bearings.
- The air bearing stage should never be operated when no air is applied. This would cause the air bearings to rub and possibly preventing them from properly floating in the future.
- The stationary magnetic assembly is highly magnetic, it should not be placed in an area where loose steel particles can be drawn into the magnetic gap.
| Examples |
Examples |
Examples |
Examples |